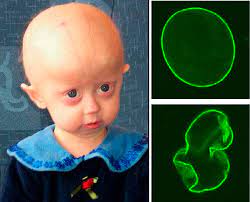
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria syndrome is a rare genetic disease that causes accelerated ageing Drug repurposing is often regarded as a cinderella child of new medicine discovery because ‘old drugs have expired patent exclusivities and the commercial opportunity is absent’. This is an erroneous view, because, in the first place, there are multiple ways to patent an […]
Drug repurposing, the development of new uses for existing drugs, is based significantly on method of use patents. That much is obvious. But for these patent applications to be granted, and defensible, they must be ‘non-obvious’, or surprising. Despite being based on literature evidence, the DrugRepurposing Online database is designed to do exactly that — […]
There have been recent developments in databases of value to drug repurposing like ChemBL and DrugBank. These are vast, free sources of information that repurposing can benefit from. But Drug Repuposing Online is different, and we wanted to tell you how it is a unique, and in our opinion, a more focused resource for repurposing, […]
While the effort to modify Alzheimer disease pathology by reducing the production of beta amyloid protein has largely been ineffective, there is a range of evidence that a widely used class of antihypertensive drug could provide a surprising benefit. Calcium antagonists are some of the most widely prescribed drugs for controlling blood pressure currently on […]
A variety of observational studies have been performed with respect to glioblastoma multiforme, the most lethal form of brain cancer, and the use of sodium valproate, an antiepileptic drug. Patients treated with sodium valproate for epilepsy have showed a improved outcome with respect to survival time and recurrence compared to patients treated with other antiepileptic...
In a recent analysis of the economics of pharmaceutical innovation, Grabowski and DiMasi calculated that out-of-pocket costs for a new chemical entity (NCE) were $1.395bn, compared to the costs for a ‘post-approval’ product of $466m. Accordingly, it may be possible to obtain three repurposed medicines for the investment in one new chemical entity. This is […]
The antidiabetic sulfonylureas, which inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) channels in pancreatic beta cells and stimulate insulin release in diabetes mellitus, mediate their effect on KATP channels via a high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor (SUR). But when looked at retrospectively in diabetic patients with ischemic stroke, patients treated with these drugs also seemd to be protected against stroke, […]